Install Emacs
2025-02-08, Sat
Install Emacs tends out to be more complicated than I thought. This log file intends to record hiccups I've encountered.
1. on Debian GNU/Linux
Debian packages are provided in separate sections1, and emacs is available in the main section. However, this package lacks all the built-in documentation, which is somehow provided in the non-free section through package emacs-common-non-dfsg. Without documentation, the claim of "self-documenting editor" doesn't stand, so a bit tweak is needed.
- Open
/etc/apt/sources.listand add "non-free" section after "main" - Run "apt-get update", as usual
- Run "apt-get install emacs emacs-common-non-dfsg"
2. on macOS
The GNU site already provides instructions to install pre-built binaries of Emacs on macOS 2, 3. Follow any one would be sufficient.
However, things became tricker when I tried to compile from source.
First, install libraries required, in reverse order:
- gnutls
- nettle
- gmp
- libtasn1
- help2man
The process was straightforward when I compiled these libraries from
source one by one, …until gnutls-3.7.11, which is the current
stable version provided on the official site4.
When compiling from the source file downloaded, there was error thrown
for file lib/system/certs.c. Turns out there is a one line change
needed in the declaration of osstatus_error, like this:
static int osstatus_error(OSStatus status)
This problem was resolved long time ago in the master branch5. So it's not like a big issue anymore. Nevertheless, the experience worths a note.
Key Takeways
- When there is error thrown while compiling source code from renowned resource, take a closer look at the error message. No need to get panic, upset, or scared.
- If a solution is found for the error, consider to submit a patch to the source repo in order to give something back to the community.
3. Notes on Common Commands
This section records common commands & keybindings for some modes, major or minor.
3.1. Global Map
| Key | Binding | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C-/, C-_, C-x u | undo | Undo some previous changes |
| C-?, C-M-_ | undo-redo | Undo the last ARG undos, i.e., redo the last ARG changes, ARGS default to 1 |
| M-. | xref-find-definitions | find definition of identifier at point |
| M-, | xref-go-back | go back to previous position in xref history |
| M-? | xref-find-references | find references to the identifier at point |
3.2. Major mode c-mode
| Key | Binding | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C-c C-e | c-macro-expand | Expand C macros in the region, using the C preprocessor |
3.3. Major mode org-mode
| Key | Binding | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C-c C-c | org-ctrl-c-ctrl-c | Multi-purpose command that does things depending on context |
3.4. Major mode emacs-lisp-mode
| Key | Binding | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C-c C-e | elisp-eval-region-or-buffer | Evaluate forms in the active region or whole buffer |
| C-M-i | completion-at-point | Perform completion on the text around point |
3.5. Major mode lisp-interaction-mode (for *scratch*)
| Key | Binding | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C-j | eval-print-last-sexp | Evalute sexp before point |
3.6. Major mode Magit
| Key | Binding | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C-x g | magit-status | open the magit work panel (i.e. magit-status buffer) for current project |
| C-x M-g | magit-dispatch | it's also bound to ? in magit panel |
| C-c M-g | magit-file-dispatch | magit operation on specific file |
Below key bindings works in magit panel
| Key | Binding | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ? | magit-dispatch | Same to C-x M-g in global map |
| & | magit-process-buffer | Show git process log |
| ^ | magit-section-up | |
| n | magit-section-froward | |
| p | magit-section-backeward | |
| C-w | magit-copy-section-value | copy the hash value of current commit |
| M-n | magit-section-forward-sibling | |
| M-p | magit-section-backward-sibling | |
| M-1 | magit-section-show-level-1-all | |
| M-2 | magit-section-show-level-2-all | |
| M-3 | magit-section-show-level-3-all |
4. Notes on Common Practices
4.1. sudo edit file
Use TRAMP mode6 to sudo open and edit file by
adding /sudo:: at the beginning of file name, e.g.
find-file (C-x C-f) /sudo::/path/to-file
4.2. Sample Init Config
Sample init config could be found in the Emacs manual7 or online8. Nevertheless, I'll put another snippet below for reference:
;; ref: ~/.emacs.d/init.el
;;
;; save & restore desktop-session
(desktop-save-mode 1)
;; enable display of line number across all windows
(global-display-line-numbers-mode)
;; show column number in the mode line
(column-number-mode)
;; disable tool-bar
(tool-bar-mode 0)
;; ============================================================
;; configs that applies to speicifc mode or
;; depends on external program
;; ============================================================
;; running external lisp from within Emacs
;; in this case, it is SBCL that is being used
(setq inferior-lisp-program "/usr/local/bin/sbcl --noinform")
;; unlock the treemacs window width
(setq treemacs-width-is-initially-locked nil)
;; MELPA
(require 'package)
(add-to-list 'package-archives '("melpa" . "https://melpa.org/packages/") t)
;; Comment/uncomment this line to enable MELPA Stable if desired. See `package-archive-priorities`
;; and `package-pinned-packages`. Most users will not need or want to do this.
;;(add-to-list 'package-archives '("melpa-stable" . "https://stable.melpa.org/packages/") t)
(package-initialize)
;; Config LSP Servers
(require 'eglot)
(add-to-list 'eglot-server-programs '((c++-mode c-mode) "clangd"))
(add-hook 'c-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(add-hook 'c++-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(add-hook 'gdscript-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(add-hook 'gdscript-mode-hook 'company-mode)
; This requires typescript-typescript-language-server to be installed through npm first
(add-to-list 'eglot-server-programs '((typescript-mode js-mode) "typescript-language-server" "--stdio"))
(add-hook 'typescript-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(add-hook 'js-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(add-hook 'js-json-mode-hook (lambda ()
(setq tab-width 2)
(setq indent-tabs-mode nil)))
(add-to-list 'eglot-server-programs '((terraform-mode) "terraform-ls" "serve"))
(add-hook 'terraform-mode-hook 'eglot-ensrue)
;; pip3 install python-lsp-server
;; program: pylsp
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
;; Start server if not already
(require 'server)
(unless (server-running-p)
(server-start))
;; Change shell flag from default "-c" to "-ic" to load .bashrc
;; (setq shell-command-switch "-ic")
4.3. Correct PATH in shell
Aside from .bashrc and .bash_profile, macOS also updates $PATH
based on content from /etc/paths.d/, which isn't recognized by
inferior shell in Emacs. This could be corrected in init.el either
through setting exec-path manually, or install package
exec-path-from-shell9 from NonGNU ELPA or
MELPA10 and introduce following content there:
;; ref: ~/.emacs.d/init.el ;; correct exec-path in inferior shell (use-package exec-path-from-shell :ensure t :init (exec-path-from-shell-initialize))
Although this package is already available through the default
nongnu archive, it is also provided on MELPA, which could be enabled
like this:
;; ref: ~/.emacs.d/init.el
(require 'package)
(add-to-list 'package-archives '("melpa" . "https://melpa.org/packages/") t)
;; Or use the melpa-stable version instead
;;(add-to-list 'package-archives '("melpa-stable" . "https://stable.melpa.org/packages/") t)
(package-initialize)
4.4. Connect to Database
Although we could connect to database in inferior shell, there is
SqlMode provided by sql.el11 to offer a dedicated
experience. Run command sql-help to see databases supported, e.g.
Use the following commands to start a specific SQL interpreter:
MariaDB: M-x sql-mariadb
MySQL: M-x sql-mysql
Postgres: M-x sql-postgres
SQLite: M-x sql-sqlite
Take PostgreSQL as an example, run sql-postgres and input connection
info (i.e. username, database, host, password, etc.) and you will end
up with a *SQL: Postgres* buffer within sql-interactive-mode.
4.5. Use LSP Server
4.6. clangd for C
clangd is a language server for C, and its official site provides
detailed guide on how to config it with eglot in
Emacs14:
(require 'eglot) (add-to-list 'eglot-server-programs '((c++-mode c-mode) "clangd")) (add-hook 'c-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure) (add-hook 'c++-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
Now we have almost real-time error message showing up along with code:
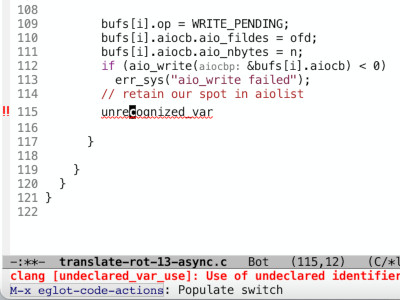
Figure 1: clangd with eglot
If the company-mode15 is also enabled for current file, we
could have code completion as well:
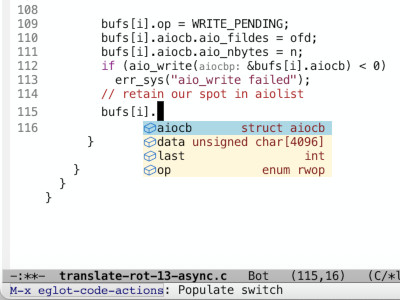
Figure 2: with company-mode enabled
4.7. gdscript-mode error
The gdscript-mode16 installed from MELPA has
the following error popped up while editing any function in the .gd
file:
self-insert-command: Symbol’s value as variable is void: electric-pair-mode
This could be resolved by giving electric-pair-mode a value manually
(or getting it into init.el):
;; turn on electric-pair-mode (electric-pair-mode 1) ;; or turn off electric-pair-mode (electric-pair-mode 0)
Also note that this problem seems to have been resolved in the latest source repo.
As for the GDScript LSP Server, it is integrated with the Godot
engine. So add following config into init.el:
(add-hook 'gdscript-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
and ensure that the Godot Engine is running before opening any .gd
file, then we should have automatic error reporting. Remember to
enable company-mode if code completion is also needed.
4.8. Set Up Common Lisp development environment
There is this online post17 that details how to set up an SBCL Common Lisp dev environment in Emacs, which could be summarized as:
- Install
SBCL18 (Steel and Bank Common Lisp) as interpreter - Install and config
Quicklisp19 for package management - Install
SLIME20 for, well,slimemode.
Now we have *scratch* buffer, ielm (inferior Emacs Lisp mode),
lisp-mode and scheme-mode all co-exist with slime, serving
different purposes.
4.9. Show keys and commands in real time
4.10. Connect to Database
We could use ad-hoc commands like sql-postgres or sql-mariadb to
connect to some database, or use the generalized command sql-connect
to manage connections to a variety of databases – with connection
details from the predefined variable sql-connection-alist, of
course. A sample of its value is listed below for reference:
(setq sql-connection-alist
'(("sample-postgres-database"
(sql-product 'postgres)
(sql-server "127.0.0.1")
(sql-user "root")
(sql-password "better-not-save-as-plain-text-here")
(sql-database "main")
(sql-port 5432))
("sample-mariadb-database"
(sql-product 'mariadb)
(sql-server "localhost")
(sql-user "mysqladmin")
(sql-database "somedb")
(sql-port 3306))
("sample-sqlite-database"
(sql-product 'sqlite)
(sql-database "/path/to/local.db"))))
4.11. Eglot show error
Eglot delegates the task of showing errors to Emacs's built-in Flymake and ElDoc.
- View error at point: with command
eldoc-doc-bufferorC-h . - List all errors in buffer:
flymake-show-buffer-diagnostics - Navigate between errors:
flymake-goto-next-errorandflymake-goto-prev-error
4.12. Abort 2 level minibuffers
Use command top-level to exit all recursive editing levels and return immediately
to the top level.
4.13. Open HTML file in Chrome through CLI
Open HTML file in Chrome through macOS CLI could be achieved through the open(1) command, e.g.
open -a "Google Chrome" index.html
4.14. Formatting JSON content
Use commands like json-pretty-print-buffer and json-pretty-print-region to get job done.
To support JSON tree folding, consider built-in package
hs-minor-mode, or tree-sitter based modern package like
treesit-fold23.
4.15. Compare Two Files
To compare two files in a side-by-side fashion, use command
ediff-files or ediff-buffers, where a dedicated new frame *Ediff
Control Panel* is brought up front for viewing control. In order to
jump between frames, use s-` or C-x 5 o for command other-frame.
4.16. Disable auto-indent
Auto-indent is provided by global minor mode electric-indent-mode, which could be
toggled globally by invoking this command. To disable it for specific mode (i.e. locally),
use electric-indent-local-mode in hook mode, e.g.
(add-hook 'typescript-mode-hook
(lambda ()
(setq tab-width 2)
(setq indent-tabs-mode nil)
(setq typescript-indent-level 2) ; (setq c-basic-offset 4)
(electric-indent-local-mode -1)
(eglot-ensure)))
Another way to achieve this is throug the electric-indent-functions, e.g.
(add-hook 'electric-indent-functions
(lambda (char)
(when (eq major-mode 'typescript-mode)
'no-indent)))
4.17. Resize windows
Window resize is achieved through a series of *-window commands. Tricky part is they are
not prefixed ones, so some of them are listed here for reference:
- balance-windows
C-x +- enlarge-window
C-x ^- enlarge-window-horizontally
C-x }- shrink-window-horizontally
C-x {
4.18. Search literal dollar sign
To search literal dollar sign in C-s, prefix $ with backslalck \, e.g. search with \$.
4.19. Freeze a window
Use function set-window-sedicated-p to mark a window dedicated to its buffer. e.g.
(set-window-dedicated-p (selected-window) t)
4.20. Display single line
To prevent a long logical lines from wrapping into multiple screen
lines, we could disable visual-line-mode and enable truncate lines
through toggle-truncate-lines. e.g.
M-x visual-line-mode M-x toggle-truncate-lines
4.21. Insert shell command output into buffer
To insert shell command output into current buffer, use the
shell-command command with prefix argument, e.g.
C-u M-!
4.22. Magit: Open file of current line in magit-satus buffer
To open the highlighted file in the magit-status buffer, invoke
command magit-diff-visit-worktree-file, which is bound to
C-<return> and C-j.
5. Appendix: Sample init.el
(global-display-line-numbers-mode 1)
(desktop-save-mode)
(tool-bar-mode -1)
(column-number-mode)
(custom-set-variables
;; custom-set-variables was added by Custom.
;; If you edit it by hand, you could mess it up, so be careful.
;; Your init file should contain only one such instance.
;; If there is more than one, they won't work right.
'(org-babel-load-languages '((emacs-lisp . t) (shell . t)))
'(package-selected-packages
'(dockerfile-mode exec-path-from-shell magit markdown-mode
terraform-mode typescript-mode yaml-mode))
'(shell-file-name "/bin/bash"))
(require 'package)
(add-to-list 'package-archives '("melpa" . "https://melpa.org/packages/") t)
(package-initialize)
;;;
(use-package exec-path-from-shell
:ensure t
:init
(exec-path-from-shell-initialize))
(require 'eglot)
(add-to-list 'eglot-server-programs '((c++-mode c-mode) "clangd"))
(add-hook 'c-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(add-hook 'c++-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(add-to-list 'eglot-server-programs '((typescript-mode js-mode) "typescript-language-server" "--stdio"))
(add-hook 'typescript-mode-hook (lambda ()
(setq tab-width 2)
(setq indent-tabs-mode nil)
(setq typescript-indent-level 2) ; (setq c-basic-offset 4)
(electric-indent-local-mode 1) ; enable indent
(eglot-ensure)))
(add-hook 'js-mode-hook (lambda ()
(setq tab-width 2)
(setq indent-tabs-mode nil)
(setq js-indent-level 2)
(eglot-ensure)))
(add-hook 'js-json-mode-hook (lambda ()
(setq tab-width 2)
(setq indent-tabs-mode nil)))
;; ref: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform-ls/blob/main/docs/USAGE.md
;; (add-to-list 'eglot-server-programs '((terraform-mode) "terraform-ls" "serve"))
(add-hook 'terraform-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
;; ref: https://github.com/python-lsp/python-lsp-server
;; pip3 install python-lsp-server
;; program: pylsp
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook 'eglot-ensure)
(require 'server)
(unless (server-running-p)
(server-start))
;;;
(setq sql-connection-alist
'(("maria-main"
(sql-product 'mariadb)
(sql-server "localhost")
(sql-port 3306)
(sql-user "mariadb"))
("postgres-main"
(sql-product 'postgres)
(sql-server "localhost")
(sql-user "postgresx")
(sql-port 5432))))
Footnotes:
About Debian package sections https://www.debian.org/distrib/packages
Instructions on installing Emacs https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/download.html#nonfree
Unofficial Emacs build for macOS https://emacsformacosx.com
GnuTLS site https://www.gnutls.org/download.html
Commit that resolved the issue https://gitlab.com/gnutls/gnutls/-/blame/master/lib/system/certs.c?ref_type=heads#L292
TRAMP Mode quick guide https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/manual/html_node/tramp/Quick-Start-Guide.html
The source repo: https://github.com/purcell/exec-path-from-shell, package on NonGNU ELPA: https://elpa.nongnu.org/nongnu/exec-path-from-shell.html
Eglot introductions:
- Eglot in Emacs manual: https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/manual/html_node/eglot/
- Eglot main page: https://joaotavora.github.io/eglot/
- Eglot repo README: https://github.com/joaotavora/eglot/blob/master/README.md
LSP Mode - LSP support for Emacs https://emacs-lsp.github.io/lsp-mode/
Config clangd with Emacs https://clangd.llvm.org/installation
Company mode home page: https://company-mode.github.io/, Company mode user manual: https://elpa.gnu.org/devel/doc/company.html
Emacs GDScript-Mode https://github.com/godotengine/emacs-gdscript-mode
Setting Up an SBCL Common Lisp Development Environment https://tomsitcafe.com/2023/10/09/setting-up-an-sbcl-common-lisp-development-environment-with-emacs-and-slime-on-debian-linux-in-2023/
Steel Bank Common Lisp https://www.sbcl.org
Quicklisp beta https://www.quicklisp.org/beta/
SLIME https://github.com/slime/slime, along with some other links:
- SLIME: The Superior Lisp Interaction Mode https://slime.common-lisp.dev
- SlimeMode https://www.emacswiki.org/emacs/SlimeMode
- SLIME-HOWTO https://www.cliki.net/SLIME-HOWTO
treesit-fold https://github.com/emacs-tree-sitter/treesit-fold